When progressive Catholics list their heroes in the church hierarchy most would include Cardinal Wilton Gregory of Washington, D.C.
When preparing their own lists, most conservative Catholics would include Archbishop Salvatore J. Cordileone of San Francisco.
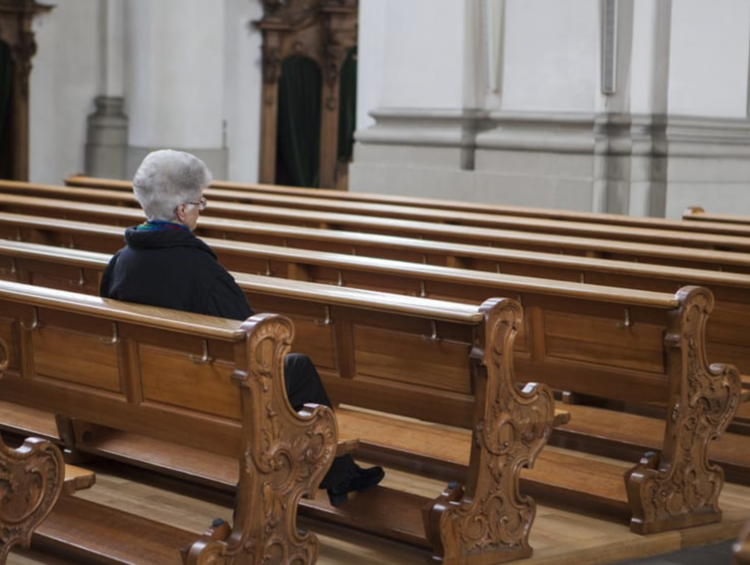
Thus, it's important to note how these two shepherds reacted to the spectacular protest staged by Catholics for Choice during the 2022 Vigil for Life inside the Basilica of the National Shrine of the Immaculate Conception.
While worshippers gathered for overnight rites and prayers before the Jan. 21st March for Life, pro-abortion-rights Catholics -- using a nearby projector -- displayed their own beliefs on the 329-foot tower and facade of America's largest Catholic sanctuary. "Catholics for Choice" appeared inside a glowing cross, accompanied by a litany of slogans, such as "Stop stigmatizing; Start listening," "Mi cuerpo, mi decision (my body, my decision in Spanish)" and "Pro-choice Catholics you are not alone."
Archbishop Cordileone released this response, via Twitter, using language implying the actions of Satan: "The attempted desecration is enormous. Diabolical. Mother Mary, pray for them, now and at the hour of death. Amen."
Cardinal Gregory's press statement pointed readers to a specific scripture to find the context for his words: "The true voice of the Church was only to be found within The Basilica. … There, people prayed and offered the Eucharist asking God to restore a true reverence for all human life. Those whose antics projected words on the outside of the church building demonstrated by those pranks that they really are external to the Church and they did so at night -- John 13:30."
That verse describes the moment when Judas exits the Last Supper to betray Jesus: "So … he immediately went out; and it was night."
Catholics for Choice offered no apologies on Twitter: "Our faith teaches us that EVERY person, including the 1 in 4 abortion patients who are Catholic, should be able to make their own decisions about their lives and bodies without interference from the church or the state. #AbortionIsEssential!!" The group's communications director, Ashley Wilson, added: "I am tired of feeling shame and stigma for being a pro-choice Catholic. And I'm not here for people to judge my own personal relationship with God."